Match configurations
DM
Use match configurations to define match rules and data groups to determine how Network MDM manages incoming data from the following:
- a source system
 A downstream system from which Network loads data., from which data will potentially be merged into the customer instance
A downstream system from which Network loads data., from which data will potentially be merged into the customer instance - a single record, manually added
- an ad hoc match
 A user-initiated match of a user-supplied file against Network data that typically results in high confidence matches., where data is compared to Network MDM data without adding or updating it
A user-initiated match of a user-supplied file against Network data that typically results in high confidence matches., where data is compared to Network MDM data without adding or updating it - deduplicating data within the instance
Match is configured similarly for each of these uses; however, because the intent of ad hoc match and source system matching can differ significantly, the specific match rules for each subscription differ.
Supported match configurations
Administrators can define data groups, match rules, and match filters for the following features:
- Ad Hoc Match Configuration – Used only for ad hoc matching. Supported for HCPs and HCOs only.
- Add Request Match Configuration - Used for all users and systems submitting add requests to a Network MDM instance.
- Match Default Configuration – Used by any subscription in a Network MDM instance.
Example
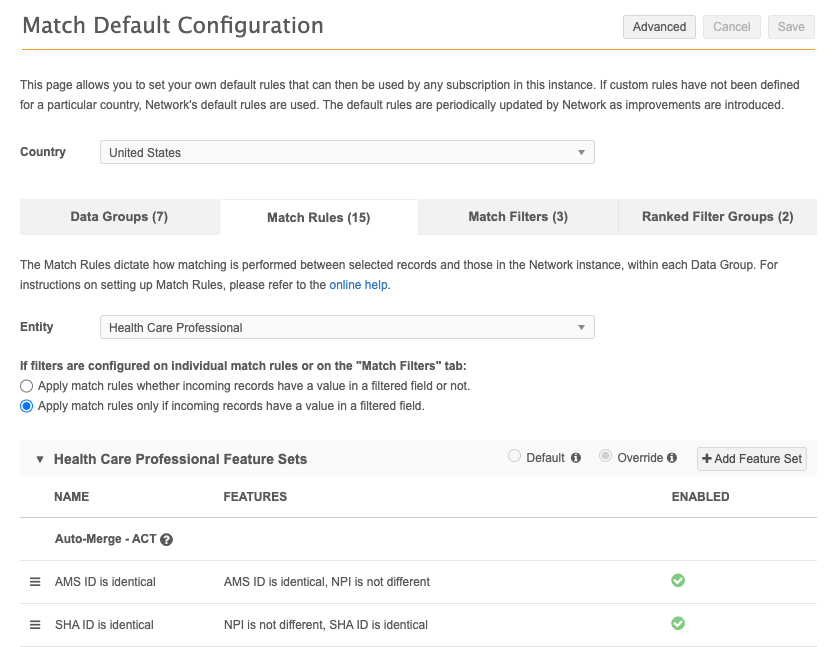
Match configurations are also configured within the following Network MDM features:
-
Source Subscriptions – Used by a specific subscription for data loading.
-
Data Deduplication - Determine if the identified records are the same as any other records in your Network MDM instance.
-
Match Rule Collections - Country groups that share custom match rules and data groups. Match rule collections can be used for source subscriptions and the Match API.
In these features, match settings display in the Match Configuration section of the subscription.
Supported objects
Veeva standard objects and custom objects are supported for most match configurations. Only Veeva standard objects are supported for Ad Hoc Match Configurations.
Note: Match rules can be defined for custom objects in Advanced Mode only.
Select a country or group
Match configurations are defined for countries.
Country groups
In match configurations, select a Country Group, consisting of one or more countries:
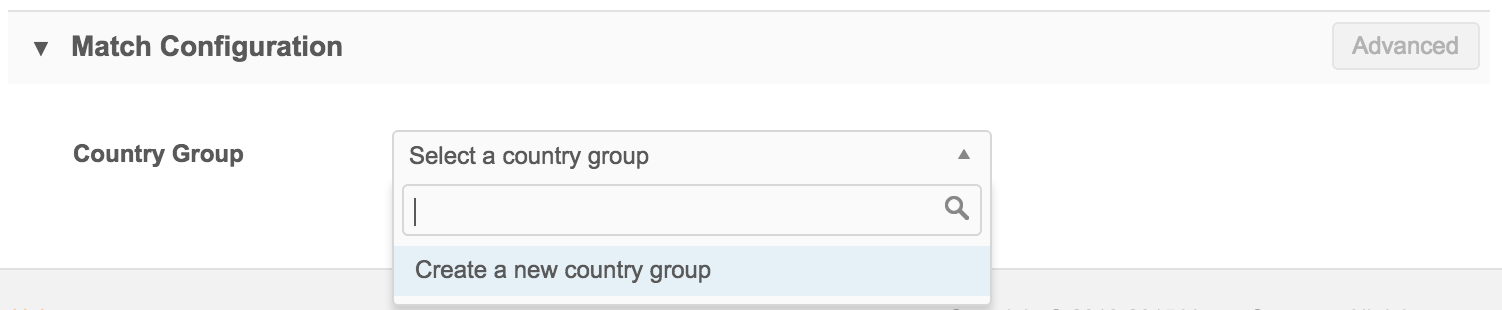
If no country group appears when you select the Country Group drop-down list, you can click Create a new country group to create one.
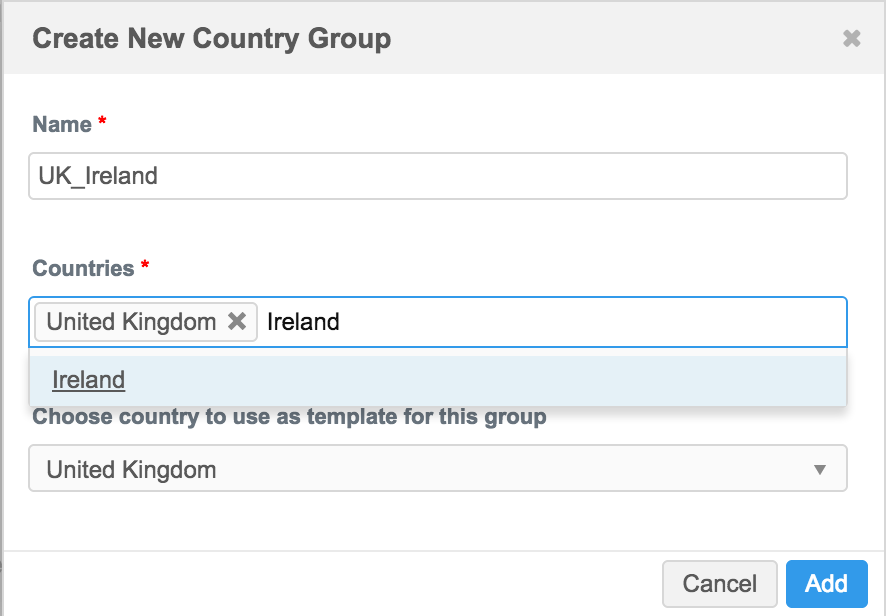
In the Create New Country Group dialog box, type a name for the group, a country or countries to include in the group, and select the country to use as the template for the group. The contents of the template is then used as the starting point for all other countries in that group.
As you type country names in the Countries field, auto-complete options appear if matching countries exist.
Configuration tabs
After the country/country group is defined, the match configuration tabs display.
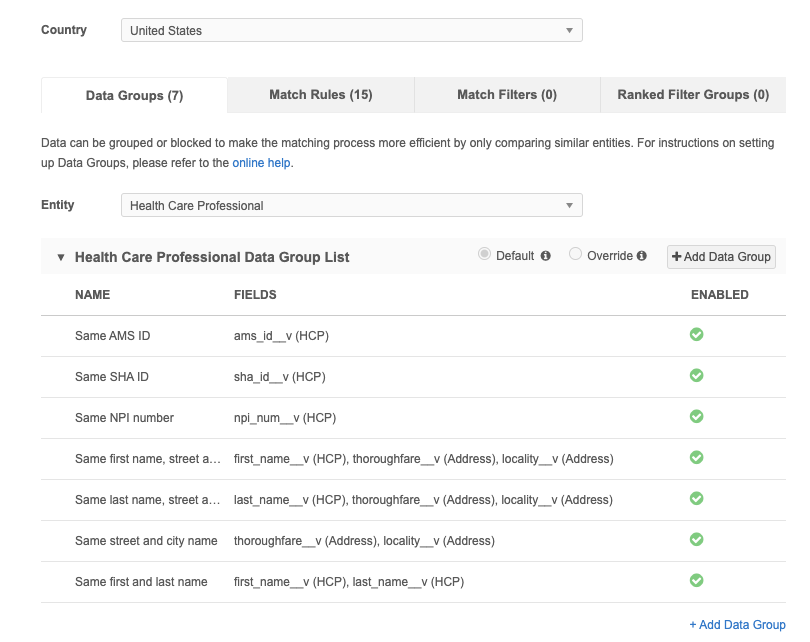
There are four tabs in match configurations:
-
Data Groups - Group similar incoming data items for comparison to streamline the match process.
-
Match Rules - Create logic to determine how matching is performed between incoming records and existing records.
-
Match Filters - Define conditions to include or exclude specific records from being considered for match pairs.
-
Ranked Filter Groups - Define conditions to include or exclude specific records from being considered in priority order.
Use these tabs to customize how incoming records are compared and matched to existing data in your Network MDM instance.
About default configurations
Network MDM provides a set of default match rules. When you view any of the match configurations for the first time, radio buttons indicate that the configuration is the default.
When the match configuration is set to Default, it will be updated automatically when Veeva introduces enhancements.
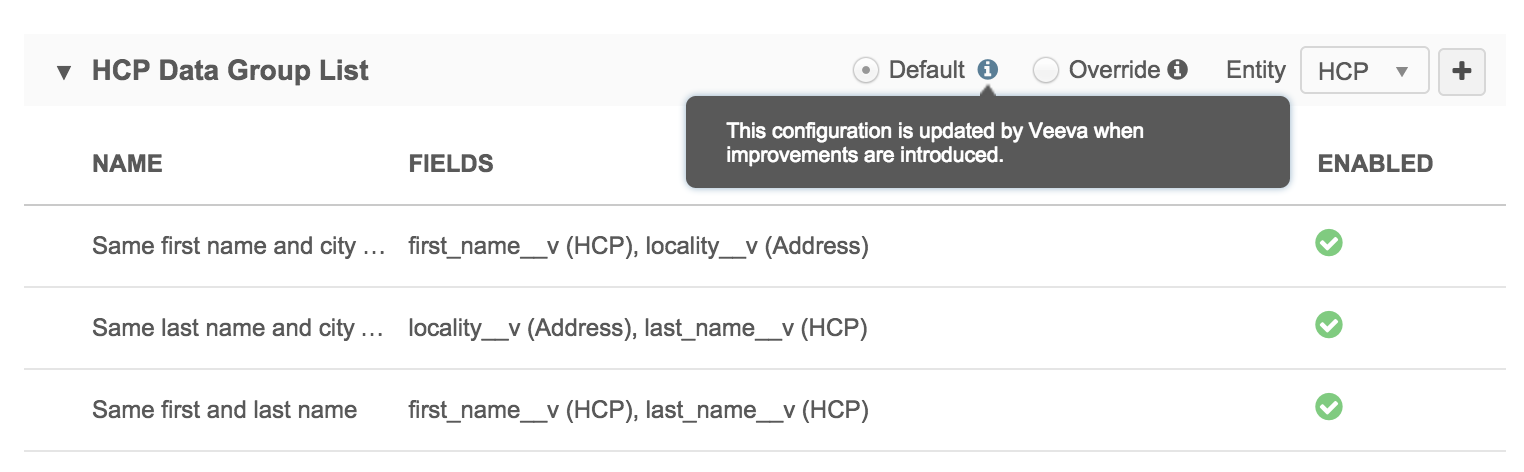
Changes to default match rules
If you make changes to the Default match configurations, Veeva will not automatically update the configuration when enhancements are introduced to avoid overriding your custom rules.
When you begin updating the match configuration, the radio button automatically switches to Override to indicate that the configuration is solely customer-maintained; Veeva will not apply enhancements to the configuration.
Important: After a configuration is customized and is no longer using the Veeva default, it cannot be reset to the default configuration.
Default match rules for custom objects
When custom objects are enabled in your Network MDM instance, default match rules are created and are accessible in Advanced mode only. The default match rules only include matching on keys because the data for your custom object is unknown to Network MDM.
Using Advanced mode
Use Advanced mode to configure data groups and match rules using XML.
Within a match configuration, click Advanced to use advanced mode. On some pages, a country must be selected before this button is enabled.
For details, see Defining match configurations in Advanced mode.
Note: Match configurations for custom objects are only available in Advanced mode.