NEX functions
This list includes functions currently supported for rule expressions.
ABS
Use to return the absolute value of a number. For example, 5 is returned as 5.
ABS(number)
| NEX | Result |
|---|---|
| ABS(-4.2) | 4.2 |
| ABS(4.2) | 4.2s |
ALL
Traverses from the parent HCP or HCO to its associated sub-object records to determine whether all of them meet the defined criteria. Returns a Boolean.
ALL(sub-object set name WHERE expression)
ALL can be used in SELECT statements.
Compact syntax can be used to combine expressions, for example, in the following example:
AT
Retrieve an element in a comma separated list of values, where index = 0 refers to the first element in the list.
AT(list, index
AT can be used in SELECT statements.
| NEX | Result |
|---|---|
| AT(['cd','ed','em','gp','hm','np','on'], 0) | 'cd' |
| AT(['cd','ed','em','gp','hm','np','on'], 2) | 'em' |
| AT(['cd','ed','em','gp','hm','np','on'], 7) | null |
Compact syntax can be used to combine expressions, for example, use with SPLIT() to split strings with a separator into a collection and then return the item in a specific position as the value of an individual field.
Example
In the following example, all_spec_cda__v = "cd,ed,em,gp,hm,np,on". Return position 0 to assign to the individual specialty_1__v field.
NEX Rule
Results
specialty_1__v = "cd"
ANY
Traverses from the parent HCP or HCO to its associated sub-object records to determine whether any of them meet the defined criteria. Returns a Boolean.
ANY(sub-object set name WHERE expression)
ANY can be used in SELECT statements.
Compact syntax can be used to combine expressions, for example, in the following example:
CEIL
Use to round a number up to the nearest whole number. For example, if the number is 4.1, 5 is returned.
CEIL(number)
| NEX | Result |
|---|---|
| CEIL(4.1) | 5 |
| CEIL(4) | 4 |
CLEANSE_STRING
Use this function with a data cleansing dictionary (lookup table) to cleanse and standardize data in text fields. For more information, see Data cleansing.
CLEANSE_STRING(field_name, 'data_cleansing_dictionary_name')
CONCAT
Combines attributes and static values. Returns a string.
CONCAT(string1, string2, string3...)
CONTAINS
Determines whether the value contains the specified characters. Returns a Boolean.
CONTAINS(string, search string)
COUNT
Traverses from the parent HCP/HCO to its associated sub-object records to determine the number of sub-objects meeting the defined criteria. Returns a number.
COUNT(sub-object set name WHERE expression)
For an HCP with a total of five addresses, two invalid and three valid:
Return five addresses:
COUNT(addresses__v)Return three addresses:
COUNT(addresses__v WHERE addresses__v.address_status__v == VALID)Return two addresses:
COUNT(addresses__v AS address WHERE address.address_status__v == INVALID)DATE
Converts the input value into a date, for example 01-31-2023. Returns a date.
STRING(DATE(value, date pattern))
The TODAY, NOW, DATE, and DATETIME functions are returned in epoch or long format, which Network will reject unless you convert the output to string using the STRING function.
For more information on date patterns, visit Oracle: Customizing Formats.
Note: For matching purposes, the STRING function must be used to convert the date to a string. If the date is not a string, it cannot be identified by the match process.
DATEADD
Enables you to add or subtract time periods to or from date values. The date parts supported are: YEAR, MONTH, WEEK, DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, and SECOND. If the integer is positive, it is added to the date. If it is negative, it is subtracted from the date. Returns date/datetime types.
DATEADD(date part, integer, date attribute)
DATETIME
Converts the input value to datetime format.
STRING(DATETIME(value, date pattern))
The TODAY, NOW, DATE, and DATETIME functions are returned in epoch or long format, which Network will reject unless you convert the output to string using the STRING function.
Date pattern format
Date patterns (for example, MM/dd/yyyy) are case sensitive. Uppercase and lowercase symbols can have very different meanings.
For more details, visit Oracle: Class DateTimeFormatter.
DELETE
Delete objects and sub-objects during data load. Sets the record state to DELETED and the status to INACTIVE, and inactivates all custom keys on the object and sub-objects.
DELETE()
Note: This function can be used only for File Preparation and Transformation rule points in source subscriptions. The function must be called before the data gets to the merge stage.
DOUBLE/LONG
Converts the input value into a number using an optional number pattern.
DOUBLE(value, number pattern)
LONG(value, number pattern)
For more information on number patterns, see Oracle: Customizing Formats.
DROP
Enables you to drop sub-objects (including address, license, and parent HCOs) under the post-merge rule point.
DROP()
This function discards the record without a warning message in the Job Details UI. If you require a message, use the REJECT function instead.
EXISTS
Traverses from the parent HCP or HCO to its associated sub-object records to determine whether any exist. Returns a Boolean.
EXISTS(sub-object set name)
FAILJOB
Causes the job to stop, with a failure code and the message you supply. Returns a log message.
FAILJOB(log message)
Total record count in feed
Fail the job if the total records in the feed are fewer than 1000.
Object record count in feed
Fail the job if there are more than 500 records for a specific object (alias name) in the feed.
Rejected record count in feed
Fail the job if more than 50% of records in the feed are rejected.
FIND
Determines the character position of a string. Returns a number.
FIND(string, search string)
In a file where the first name and last name are in one column in the format "last name, first name" you would use:
First name = RIGHT(NAME, FIND(NAME, ',')+1)
FLOOR
Use to round a number down to the nearest whole number. For example, if the number is 4.9, 4 is returned.
FLOOR(number)
| NEX | Result |
|---|---|
| FLOOR(4.9) | 4 |
| FLOOR(4) | 4 |
GETOBJECTNAME
Use to check the entity type of the record. Available to use in source subscriptions and custom fields.
GETOBJECTNAME()
Important: This function is the same as GETTARGETTYPE(), but GETTARGETTYPE() is not supported in the NEX Tester. Use GETOBJECTNAME() instead.
Use the function on a custom field to concatenate the entity type with a value; for example, the Network ID.
GETTARGETTYPE
Check the entity type of the record. Available to use in source subscriptions and custom fields.
GETTARGETTYPE()
Note: If the function is used in the File Preparation stage, the item type (alias name) is returned because the object is not yet mapped to the Network object type in that stage. For example, you might see ACCOUNT returned in the File Preparation stage, which will be mapped to HCP or HCO in a later stage.
Use on a custom field to add an alternate key to HCP and HCO records. The format of the alternate key is determined by the entity type of the record. For example, if the entity type is HCP, prefix the key with HCP (HCP-<ID_number>).
Use the function on a custom field to concatenate the entity type with a value; for example, the Network ID.
Note: GETTARGETTYPE is not supported for the NEX Tester. Use GETOBJECTNAME instead.
IF
Enables you to evaluate an expression that returns a Boolean value, and to specify what action to take, depending on that value. If you do not provide a False action, no action is performed when the expression evaluates to False. Returns value type based on the condition.
IF(condition, value if true, value if false)
Note: You cannot make assignment statements within the value if true or value if false parameters. You can, however, use the REJECT function.
Using the above example, the following would not work:
INVALIDATE
Sets the record state to INVALID (effectively removing it from Network) and the status to INACTIVE, inactivates all custom keys, and invalidates any related sub-objects for the record.
INVALIDATE()
Note: This function can be used only for Transformation rule points in source subscriptions.
Invalidate based on status:
Invalidate based on address type:
ISEMPTY
Same as ISNULL with the addition that if the value is blank ("") the function will also return True.
ISEMPTY(string)
ISNEWOBJECT
Indicates if the object is new to the system. Returns a Boolean.
ISNEWOBJECT()
ISNULL
Determine whether an attribute contains a value. In the subscription, you define how NULL is defined by the source. Based on that definition, this function returns true if the value is considered to be NULL by Network. Returns a Boolean.
ISNULL(any)
ISVALIDREF
Compares a value to a list of network codes for a given reference type. If the system is populated, it will leverage the aliases provided the ordering of entity model rules is "entity.model.rules": "network:nex, network:normalize_table, network:normalize_alias, network:normalize_cleanup".
ISVALIDREF(reference type, code).
JOIN
Use this function to format an array of values using a delimiter. Empty text strings are ignored.
JOIN(<collection>,<separator>)
Note: This can be used with the LOOKUP and LOOKUPN functions.
Note: Format the returned array so each value is separated by a pipe (|).
This returns the following result: "abc|Edgar|def|Elum"
LEFT
Parses out the number of defined characters from the left. Returns a string.
LEFT(string, number)
LEN
Returns the length (in characters) of an attribute. Returns a number.
LEN(string)
LOGDETAILWARN
Displays a warning in the job history for any record failing certain criteria.
Note that this is not specifically for lookups. It can be used for other NEX functions also, for example, REJECT().
[
"IF(LOOKUPVALIDATE('addressdata__t', postal_code__v: UPPERCASE('a12b3c'), locality__v:'springfield', administrative_area__v: concat('NY', 'C')), LOGDETAILWARN('The address combination is incorrect'))"
]
LOOKUP
Used for lookup tables only.
Use to look for a value from a range (one or multiple columns in a row) and then returns a value in the same row. Returns the first value that is found in the table.
LOOKUP('lookup_table_name', 'column_name', <lookup_column_1>: <expression1>, <lookup_column_2>: <expression2>)
-
column_name - The column in the lookup table that the data will be returned from.
Create a lookup table that maps HCP Type to record type.
Lookup table (type_mapping__t)
| hcp_type | record_type |
|---|---|
| P | HCP |
| N | HCP |
| R | HCP |
| O | HBP |
| STAFF__C | HBP |
NEX rule
Results
-
If the HCP Type is P (Prescriber), return HCP.
-
If the HCP type is O (Business Professional), return HBP.
Support for field collections
A collection of fields can now be referenced in LOOKUP or LOOKUPN functions for NEX rules.
You can include some of the specialty set of fields (specialty_1__v to specialty_10__v) in the LOOKUPN() function.
LOOKUPN
Used for lookup tables only.
Use this function to lookup all values matching a key in a lookup table.
For example, you can use the functions to store a product family in a custom field. Returns all matching values on the table; by default, returns 100 results. Specify a parameter to limit the number of lookups returned. The maximum limit is 500 values. If more than 500 is defined, the NEX rule automatically fails. In a source subscription, the job will complete, and the error displays in the Job Error Log.
Tip: To ensure that the array returned by LOOKUPN can be easily managed in a field or another calculation, always use JOIN with LOOKUPN.
LOOKUPN('lookup_table_name', 'column_name', <limit_parameter>, <lookup_column_1>: <expression1>, <lookup_column_2>: <expression2>)
-
column_name - The column in the lookup table that the data will be returned from.
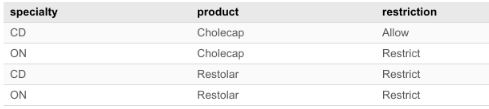
Lookup table (spec_matrix__t)
| specialty | product | restriction |
|---|---|---|
| CD | Cholecap | Allow |
| ON | Cholecap | Restrict |
| CD | Restolar | Restrict |
| ON | Restolar | Restrict |
NEX rule
Results
-
Finds restricted products for an HCP who's specialty is ON (Oncology)
Returns: ['Cholecap','Restolar']
-
Finds restricted products for an HCP who's specialty is CD (Cardiovascular Disease)
Returns: ['Restolar']
Note that a collection is returned. To generate a string that is delimited from the collection, use the JOIN function with LOOKUPN.
Note: If a field contains an empty value, the empty value is returned in the results. For example, if the lookup returns two values but the first value is null, the null value and separator displays with the text value.
LOOKUPVALIDATE
Used for lookup tables only.
Use to look for a value from a range (one or multiple columns in a row). Returns TRUE if value found, FALSE otherwise.
LOOKUPVALIDATE('lookup_table_name',<lookup_column_1>: <expression1>, <lookup_column_2>: <expression2>)
This example uses a lookup table called spec_matrix__t.
Lookup table
| specialty_code | specialty_name | cholecap | restolar |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD | Cardiovascular Disease | Allow | Restrict |
| ON | Oncology | Restrict | Allow |
NEX rule
Leverage one specialty field:
Leverage two specialty fields:
Results
-
If the HCP's specialty is CD, then the NEX rule will return FALSE.
-
If the HCP's specialty is ON, then the NEX rule will return TRUE.
LOWERCASE
Sets all characters to lowercase. This cannot be applied to Veeva-owned fields in the local instance. Returns a string.
LOWERCASE(string)
MAX
Returns the highest value specified. Each value must be of the same type; for example, date. NULL values are ignored unless all are NULL, in which case NULL is returned. Accepts string, number, or date/datetime types.
MAX(value1, value2, value3...)
MAX(created_date__v, NOW()) (suitable if the object is being updated, and has not just been created)MAX(DATE('12-12-2000', 'MM-dd-yyyy'), grad_trg_end_date__v)MID
Parses out the number of defined characters from the defined midpoint. Returns a string.
MID(string, number, number)
MIN
Returns the lowest value specified. Each value must be of the same type; for example, date. NULL values are ignored unless all are NULL, in which case NULL is returned. Accepts string, number, or date/datetime types.
MIN(value1, value2, value3 ...)
Suitable if the object is being updated, and has not just been created:
NOW
Returns both the date and time in GMT.
STRING(NOW())
Note: The TODAY, NOW, DATE, and DATETIME functions are returned in epoch or long format, which Network will reject unless you convert the output to string using the STRING function.
returns:
PROPERCASE
Sets value to its proper case. This cannot be applied to Veeva-owned fields in the local instance.
PROPERCASE(string)
REGEXCONTAINS
Enables you to use regex to identify aspects of the value. For more information on regex syntax, visit Oracle: Class Pattern.
REGEXCONTAINS(string, regex)
REGEXREPLACE
Enables you to use regex to update aspects of the value. For more information on regex syntax, visit Oracle: Class Pattern.
REGEXREPLACE(string, regex, replacement)
REJECT
Rejects the record and generates a job warning. If you do not provide a log message, the rule syntax appears with an explanation for the rejection. Adding a log message helps significantly with troubleshooting.
REJECT(log message*)
RIGHT
Parses out the number of defined characters from the right. Returns a string.
RIGHT(string, number)
ROUND
Use to change a number to the closest whole number. If the number ends in .5 (for example, 4.5), it always rounds up.
ROUND(number)
| NEX | Result |
|---|---|
| ROUND(3.14) | 3 |
| ROUND(3.5) | 4 |
| ROUND(3) | 3 |
| ROUND(3.14159*10)/10.0 | 3.1 |
| ROUND(3.14159*100)/100.0 | 3.14 |
SETI
Loads dynamic attribute data from Veeva CRM or Vault CRM.
Veeva CRM example
FIELD =if(Dynamic_Attribute_Label_vod__c == 'Key_Account', 'key_account__c'),
SETI(field, Dynamic_Attribute_Value_Checkbox_vod__c)Vault CRM example
FIELD =if(dynamic_attribute_label__v == 'Key_Account', 'key_account__c'),
SETI(field, dynamic_attribute_value_checkbox__v)For more information, see Loading dynamic attribute data.
STRING
Converts the input value into a string. This is typically used to prepare data for Network. Other conversion functions are used to prepare a value to go through another function. The pattern is optional, depending on the value.
STRING(value, pattern)
SPLIT
Use to split strings into a collection and then join appending/concatenating/updating values.
SPLIT(string, separator)
Split a string with a separator into a collection.
NEX Rule
Results
["cd","ed","em","gp","hm","np","on"]
Use with AT() to return an item at a specific position in the collection. For example, assign that item to an individual field.
STRINGSORT
Returns a collection of elements based on the defined sort order.
STRINGSORT(collection, sortOptions)
Parameters
-
collection (for example, ['Z', 'a', 'b'])
-
sortOptions - asc (default) or desc
Null elements are ignored. String sort is not case-sensitive.
Returns
[CA, co, DEA, NY, WA]
Returns (for Oncology HCPs)
[‘Restolar’, ‘Cholecap’]
TABLEEXIST
Checks for the existence of a lookup table and returns TRUE if exists, FALSE otherwise.
Note: Use only as a Feed Acceptance rule.
TABLEEXIST('lookup_table_name')
TODAY
Returns the current date at midnight in GMT. Uses the date format.
STRING(TODAY())
Note: The TODAY, NOW, DATE, and DATETIME functions are returned in epoch or long format, which Network will reject unless you convert the output to string using the STRING function.
returns:
TRIM
Returns the original value with the whitespace removed.
TRIM(string)
UPPERCASE
Sets all characters to uppercase. This cannot be applied to Veeva-owned fields in the local instance.
UPPERCASE(string)