Step 3: Define optional events for the search widget
The search widget is completely functional for business users to view records when the two provided code blocks from Network have been added to your internal application. However, you can customize the behavior of the widget to meet your business needs. Web developers can define events which return a JSON response so you can use the data in your downstream systems.
Events are triggered when users perform an action in the search widget.
Download record events
Define an event so users can download records from the search widget to your internal application. By default, if the user clicks the Select button on the search result, the record is downloaded to your Network instance. Downloading the record to the internal application enables users to complete transactions on the record; for example, adding the HCP to an expense report.
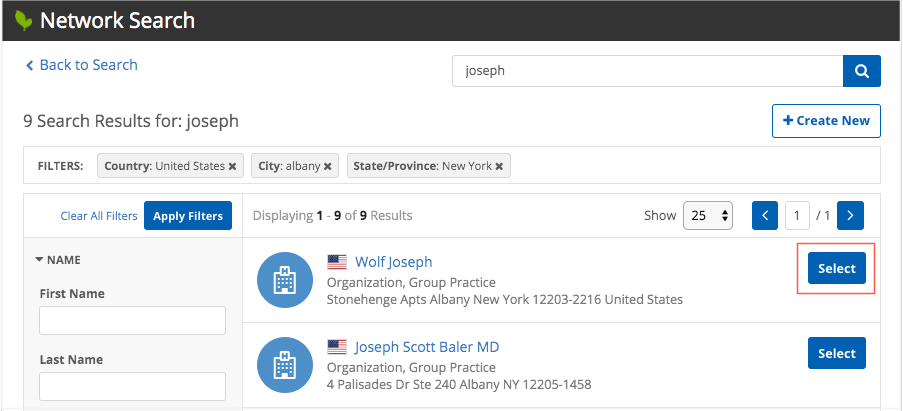
Event: select
Web developers can define a select event to trigger when users click the button beside the search result. When the event triggers, a JSON returns the primary information for the selected record (HCP or HCO); for example, name, Network ID, addresses, licenses, parent HCOs, alternate keys, and custom keys. Web developers can customize the JSON so that the record can be added to your downstream system.
More information, along with code samples, is available on the Veeva Network developer site at https://developer.veevanetwork.com/widgets/.
Add request events
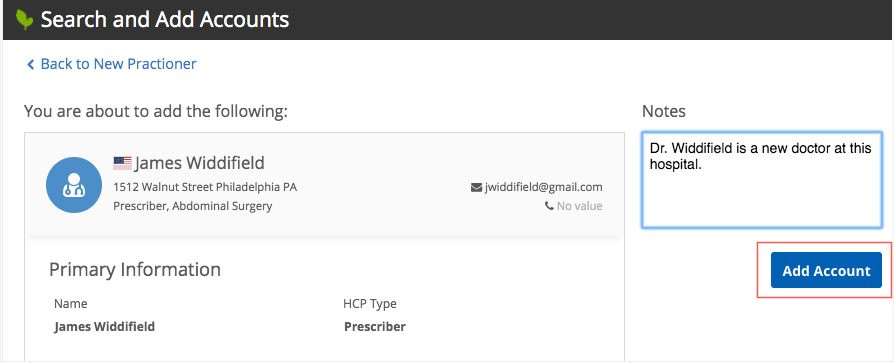
If your search widget supports creating add requests, two events can be defined so the task information is returned so it can be stored in your downstream system. The events are triggered when users click the Add Account button to submit a new record.
By default, when users click the button, add requests are routed to data stewards to validate, but users are able to immediately action the record in your internal application. After the add request is processed, the record is added to your Network instance.
Event: dcr-presubmit
The dcr-presubmit event provides the data from the add request. This includes the creator (user that submitted the add request), the comments from the Notes section, and all of the new field values that the user provided for the record and the associated sub-objects (addresses, licenses, parent HCO affiliations). When users click Add Account, a JSON response can return this data. Developers can customize the JSON so the data can be stored in your downstream system.
Event: dcr-submitted
The dcr-submitted event provides the task ID in a JSON response for the submitted add request.
Event: select
When the select event triggers, a JSON returns the entire record information for the selected record (HCP or HCO); for example, name, Network ID, addresses, licenses, parent HCOs, alternate keys, and custom keys. This is the same as the select event for downloading a record.
Web developers can retrieve the task ID from the JSON so it can be stored in your downstream system.
Using reference aliases
Network reference codes are returned in the JSON by default.
Reference aliases can be used so the JSON returns data that your downstream system will understand. For example, the Network reference code for New York state is US-NY. If your downstream system identifies New York state as NY, you can create that reference alias in Network so the JSON returns NY.
Reference aliases are specific to source systems, so administrators can create the mapping for the system that you specify in the widget configuration.
For more information about mapping Network codes to values for your downstream, see Reference aliases.
Prefill search terms
When the Search widget is embedded in your internal application, it can be configured to do the same search most recently performed in your app. Web developers can add properties to the widget code to populate the widget with the same search terms.
For example, before adding an account, business processes might require you to search a downstream system like Service Cloud for an existing account. If a match isn't found, you can use the Search widget to see if the account exists in Network or OpenData. To avoid entering the same data twice, the Search widget can be set to automatically search for the terms that you just entered in your downstream system.
Note: The Search widget configuration must support the Advanced Search form.
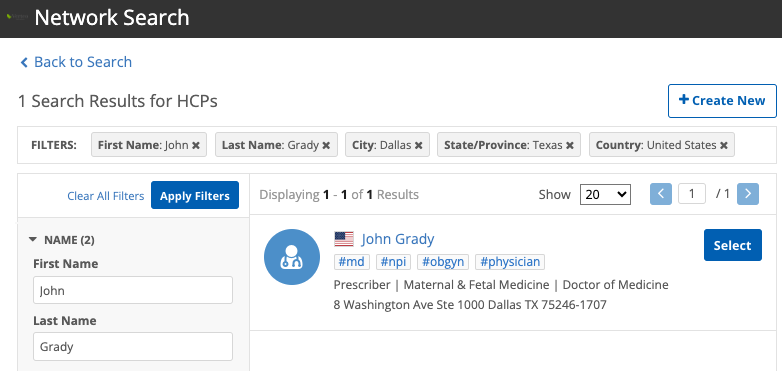
Example
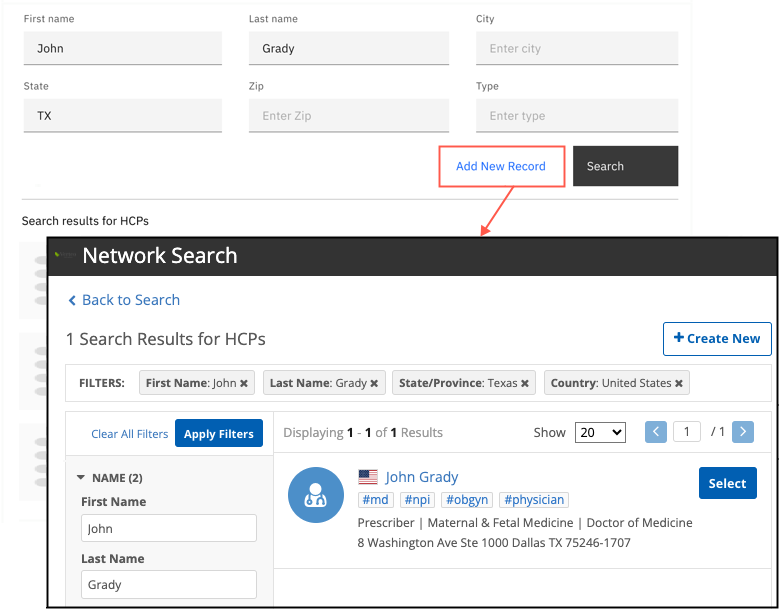
In this example, the search widget is embedded in an internal application. After a user searches locally for an HCP, they can launch the Search widget to search Network and OpenData for that HCP.
The Search widget is configured to prefill the search form and automatically search for the terms that the user already entered in their internal app.
When the Search widget opens, the search results automatically display for those search terms.
Widget properties
Use the following properties in the Search widget code:
-
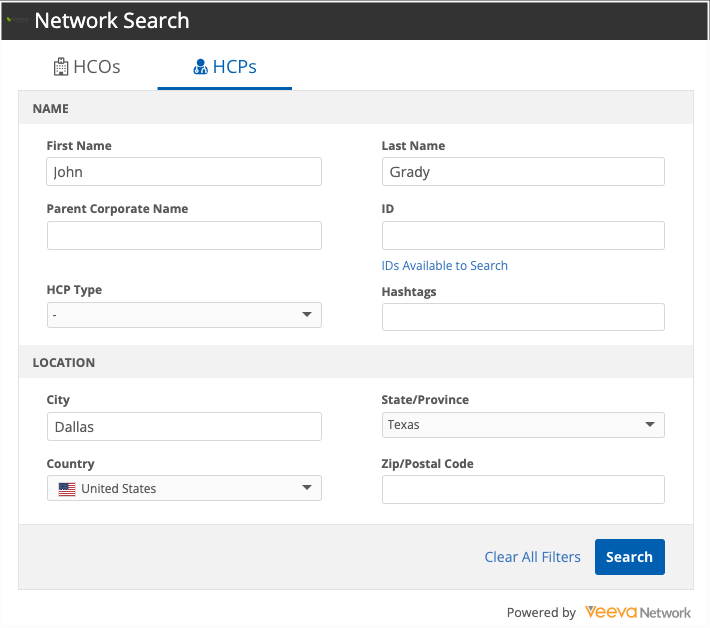
pre-fill-search-form - Use this property to prefill the Search widget advanced form with the search terms that were used in your downstream system.
When the user open the Search widget, the Advanced search form displays with the pre-filled search terms. The user can add criteria and then click Search to view the results
-
auto-search - Use this property with the pre-fill-search-form to prefill the search form and automatically open the widget to the search results page.
Note: The auto-search property cannot be added to the widget code without the pre-fill-search-form property.
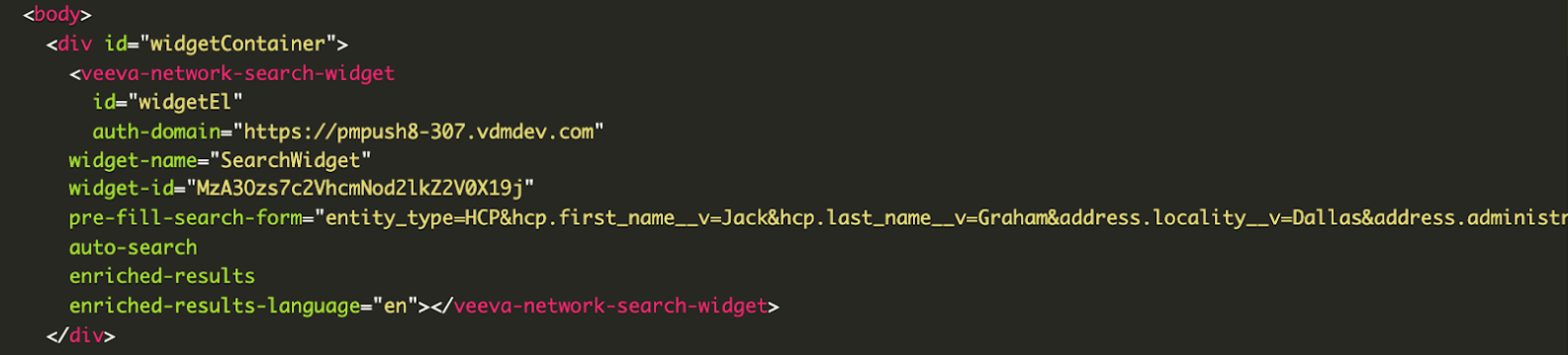
Add the properties
Web developers can add the properties to the veeva-network-search-widget element in the widget code.
Example widget code
Supported searches
When these properties are added, the search terms that you use in the downstream system must match the fields used in the Search widget.
Supported values
-
Entity type - Must be HCP or HCO.
If entity_type is not defined or is not HCP or HCO, the property is ignored.
Supported fields
All standard and custom fields for Veeva objects (HCP, HCO, Address, License, Parent HCO) are supported if they are used in the Advanced search form.
HCP Example
entity_type=HCP&hcp.first_name__v=Jack&hcp.last_name__v=Hughes&address.locality__v=Chicago
HCO Example
entity_type=HCO&hco.corporate_name__v=Barnes%2ASmith&address.locality__v=Chicago
Special fields
These fields are supported:
-
ID__s - Search by ID field
-
hashtags - Search by hashtag
Additional considerations
-
Each term is separated by the ampersand (&) symbol.
-
If a term has spaces, symbols, or special characters, they must be encoded.
-
All other fields are ignored.
| < Step 2: Embed the search widget | Developers: Configure your web application > |